What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are a very broad range of chemicals that interact with the endocannabinoid system. Beyond their ability to interact with cannabinoid receptors in your body, cannabinoids do not necessarily share other similarities with each other. For example, not all cannabinoids share the same structure or have the same effect on the body.
Different cannabinoids have different cannabinoid effects. Nor do they all come from the same natural sources. In fact, some cannabinoids are synthetic, meaning that they are manufactured rather than extracted from a natural source.
While the word can refer to cannabinoids from any source, it is commonly associated with the cannabinoid chemicals found in cannabis and hemp plants, and the effects produced by using cannabis. This is because cannabis is a very rich source of these compounds. Depending on the strain of the plant, cannabis can contain up to 100 cannabinoids.
The most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis are THC and CBD. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, otherwise known as THC, is the cause of the psychoactive effects of marijuana. Cannabidiol, or CBD, has no such effect but is responsible for many of the therapeutic effects that people can experience from cannabis or CBD use.
Types of Cannabinoids
Here’s a list of the major known cannabinoids.
CBD
CBD or cannabidiol is a chemical that can be extracted from either cannabis or hemp plants and is often sold in marijuana dispensaries as an oil or dietary supplement, as well as many other forms such as drinks, topical lotions, and more. Not all cannabis plants provide significant amounts of CBD, regardless of how many other cannabinoids they contain, such as THC.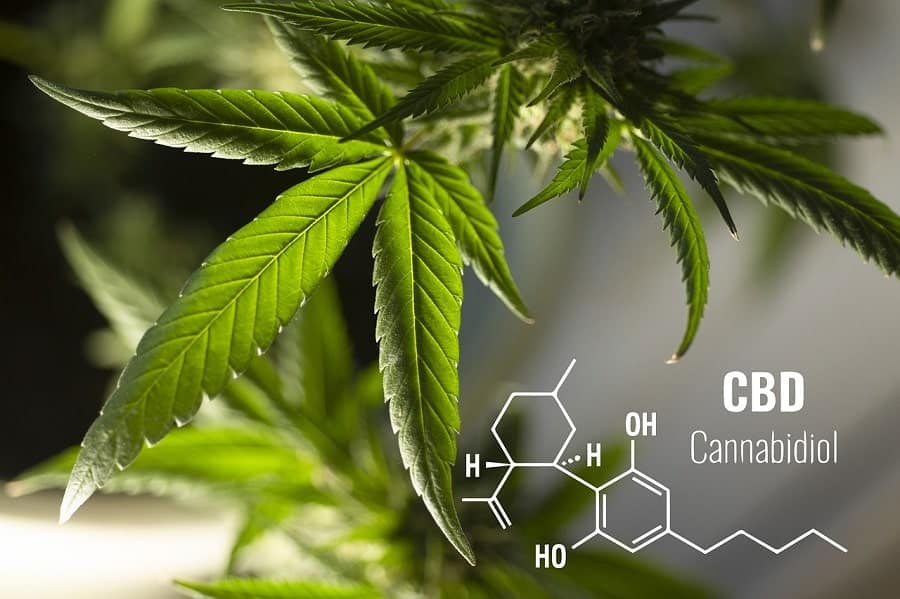
CBD is commonly used to provide various therapeutic effects without any of the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis products that also contain THC. Cannabinoid receptors play a role in regulating appetite, sleep, pain, and immune system responses. As a result, many CBD users report reduced inflammation, chronic pain, and anxiety because of CBD use, as well as improved appetite and sleep.
CBDA
Cannabidiolic acid, or CBDA, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is a precursor to CBD. When CBDA is heated it decarboxylates to become CBD. This happens instantly when smoking or vaping, or more slowly when plant material is left to dry.
However, CBDA itself can also confer benefits when consumed before it has been turned into CBD. While less studied than CBD, research into CBDA has found it to potentially be more effective as an anti-depressant and anti-nausea drug than CBD.
CBG
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is often known as the mother of all cannabinoids, as other cannabinoids are derived from the acidic form of cannabigerol, cannabigerolic acid. Like CBD, CBG may have benefits as an anti-inflammatory, however, its potential benefits for humans have yet to be thoroughly researched.
CBG is only found in small quantities in most cannabis products. While most products are made or extracted from mature plants, CBG is only present in large quantities in younger plants. As a result, high-CBG strains are typically the result of extensive cross-breeding and genetic manipulation.
CBC
Cannabichromene, or CBC, is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid with a number of potential health benefits and has been suggested to work synergistically with other cannabinoids. In other words, CBC may increase the anti-inflammatory or pain relief effects of other cannabinoids such as CBD. Early research has also shown CBC to be one of the most effective cannabinoids at inhibiting the growth of new cancer cells.
CBN
Cannabinol, or CBN, is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that, similarly to THC, is produced by the oxidization of THCA. CBN is commonly used as a sedative or to aid sleep. Like many other cannabinoids, research has shown that consuming CBN can help regulate the immune system to reduce inflammation and reduce chronic pain. As a result, it is one of the cannabinoids often used by people with conditions like arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
THC
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is by far the most well-known cannabinoid found in cannabis and is the primary chemical responsible for the intoxicating effects associated with smoking, vaping, or otherwise consuming cannabis plants and extracts. It is one of the products of oxidizing THCA.
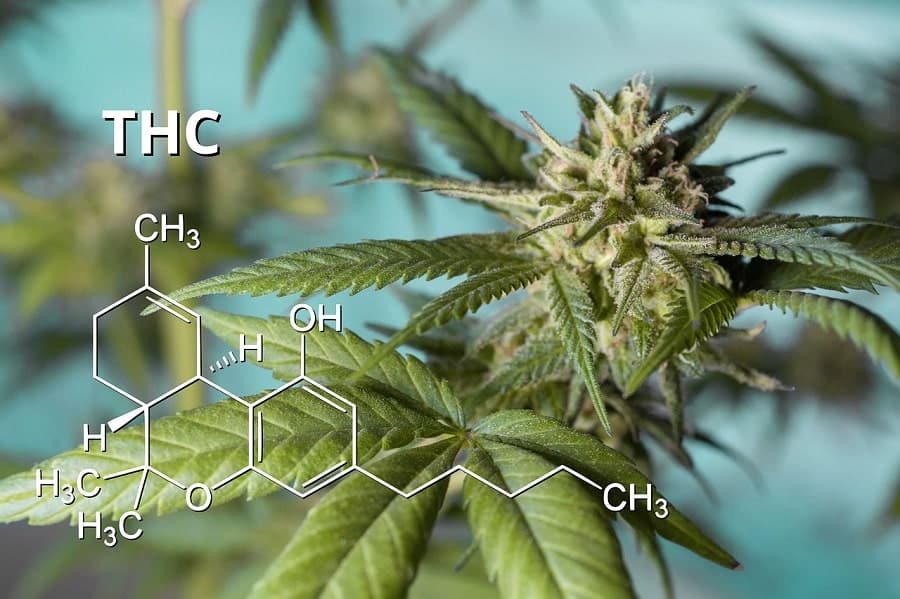
While THC is often associated with its psychoactive properties and the recreational use of marijuana, THC can also be an effective suppressant of pain and nausea. It also helps to protect your brain cells from damage, and studies have shown that THC can ease a range of symptoms experienced by people suffering from PTSD, such as agitation, depression, and insomnia, and reduce the occurrence of flashbacks and nightmares.
THCA
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THCA, is a precursor chemical to several other cannabinoids, including THC. Unlike THC however, THCA is not a psychoactive cannabinoid. Early studies suggest that it may confer many of the same health benefits as THC, but without the intoxicating effect, making it potentially more useful as a treatment for inflammation and nausea.
While any cannabis strain that contains THC technically contains THCA, heating cannabis flower by smoking or vaping will convert that THCA into THC. Instead, THCA is commonly consumed via drinks and tinctures made with juiced raw cannabis plant matter.
THCV
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV, is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid with somewhat different cannabinoid effects compared to other cannabinoids. These include reduced appetite and increased satiety after eating, as well as a boost to energy metabolism. These effects make it useful for managing or losing weight, as well as managing type 2 diabetes.
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, also known as Delta-8 THC or simply Delta-8, is a close cousin to THC that produces many of the same effects. It is considerably less potent than THC as an intoxicant, however, though it still produces a similar psychoactive effect.
Delta-10 THC
Delta-10-tetrahydrocannabinol, or Delta-10 THC, is another cannabinoid that offers similar effects to THC, with milder and more relaxing psychoactive properties. They are also commonly used by people looking for a less intense experience.





