What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Cannabis, and the products derived from it such as CBD oil, has a broad range of effects as it contains chemicals that interact with a system in the human body that regulates many vital processes. This system is called the endocannabinoid system.
Although it was only discovered within the last 30 years, understanding the endocannabinoid system could be key to understanding and utilizing the medicinal and therapeutic potential of cannabis and cannabis extracts. But what exactly is the endocannabinoid system, and how does it work?
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a complex signaling system that the cells in your body use to communicate. The endocannabinoid system was only discovered in the early 1990s. As a result, experts are still studying the system to understand what it does and how it works.
While not yet fully understood, the endocannabinoid system is known to play a role in regulating a wide range of functions throughout the body, such as sleep, memory, appetite, and mood. Because of this, cannabinoid chemicals found in cannabis and other plants may have effects on the body due to their interactions with the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoid System Structure
The endocannabinoid system is comprised of three main components. These are:
Cannabinoid Receptors
Endocannabinoid receptors are found throughout the body. Cannabinoids in the body can bind to these receptors, signaling to the endocannabinoid system to perform different functions according to the cannabinoid chemical binding to the receptor.
There are two main types of cannabinoid receptors. CB1 receptors are mainly found in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors mostly exist in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells.
Enzymes
Enzymes break down cannabinoids once they have completed their function of binding to cannabinoid receptors so that the receptors are available for further signals.
Endocannabinoids
Endogenous cannabinoids, or endocannabinoids, are cannabinoid chemicals that are produced by your body. Your body produces them as needed for various functions in the body, and researchers have yet to clearly establish what the healthy levels of the few known endocannabinoids should be.

What Does the Endocannabinoid System Do?
As previously mentioned, a full understanding of the endocannabinoid system and its various functions has not yet been fully established. It has been linked to many processes throughout the body, including:
- Appetite and digestion
- Metabolism
- Chronic pain
- Inflammation and other immune system responses
- Mood
- Learning and memory
- Motor control
- Sleep
- Cardiovascular system function
- Muscle formation
- Bone remodeling and growth
- Liver function
- Reproductive system function
- Stress
- Skin and nerve function
These functions all contribute to the stability of your body’s internal conditions, also known as homeostasis. If this balance is disrupted by illness or injury, the endocannabinoid system is part of the body’s response to restore the balance and return your body to healthy operation. It does more than just respond to damage or infection, however.
The endocannabinoid system is regulating your body in this way all the time. It decides when you need to sweat when you need to feel hungry, and many more details that keep your body in a healthy balance throughout the day.
This is currently believed to be the primary purpose of the endocannabinoid system.
Several health conditions are now believed to be a result of endocannabinoid deficiencies or dysfunction of the endocannabinoid system. As a result, cannabinoids from plants such as cannabis, known as phytocannabinoids, are the subject of medical research to investigate their uses in managing the endocannabinoid system.
How do phytocannabinoids work with ECS?
While endocannabinoids are cannabinoids that come from within the body, phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids that come from plants, most notably cannabis, from which they derive their name. Some phytocannabinoids can interact with the human endocannabinoid system to produce various effects depending on the particular chemical. The cannabis plant is a rich source of some of the more potent phytocannabinoids with effects on the human body, such as THC and CBD.
Much like with endocannabinoids, the effect that a phytocannabinoid has on your body when it binds to a cannabinoid receptor varies depending on the phytocannabinoid in question.
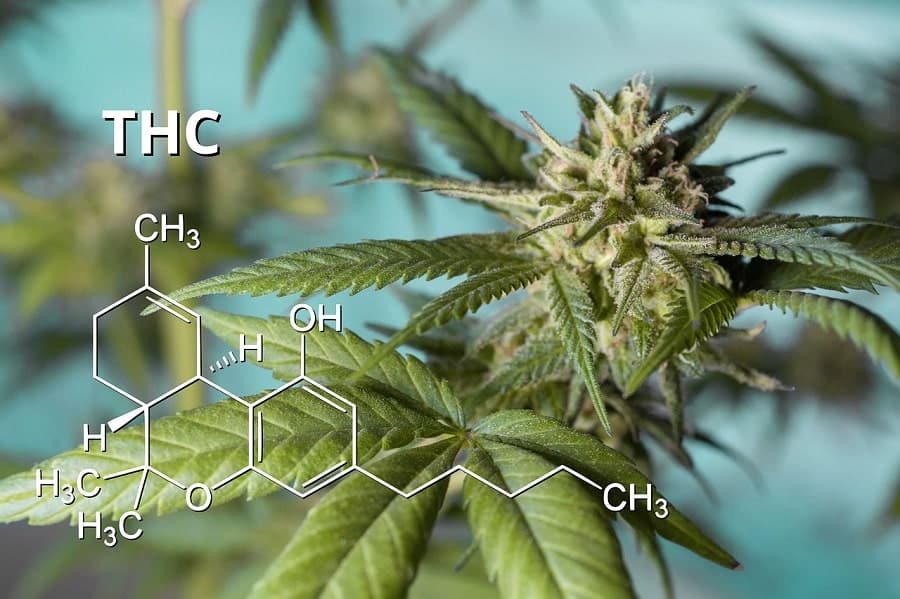
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive phytocannabinoid found in cannabis and is responsible for most of its intoxicating effects. THC can bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors. As a result, it can have significant effects on both the body and the mind. Its effects include pain and nausea relief, improved sleep, and appetite stimulation.
THC has notable psychoactive properties, which may be desirable for recreational use but make it unsuitable as a long-term medicinal solution. As a result, people seeking the therapeutic effects of THC often prefer non-intoxicating alternatives such as THCA, CBD, and other phytocannabinoids found in cannabis plants.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is another well-known phytocannabinoid found in cannabis. Unlike THC it has no intoxicating effects and is commonly used to tackle pain, inflammation, nausea, and anxiety. CBD does not bind to cannabinoid receptors.
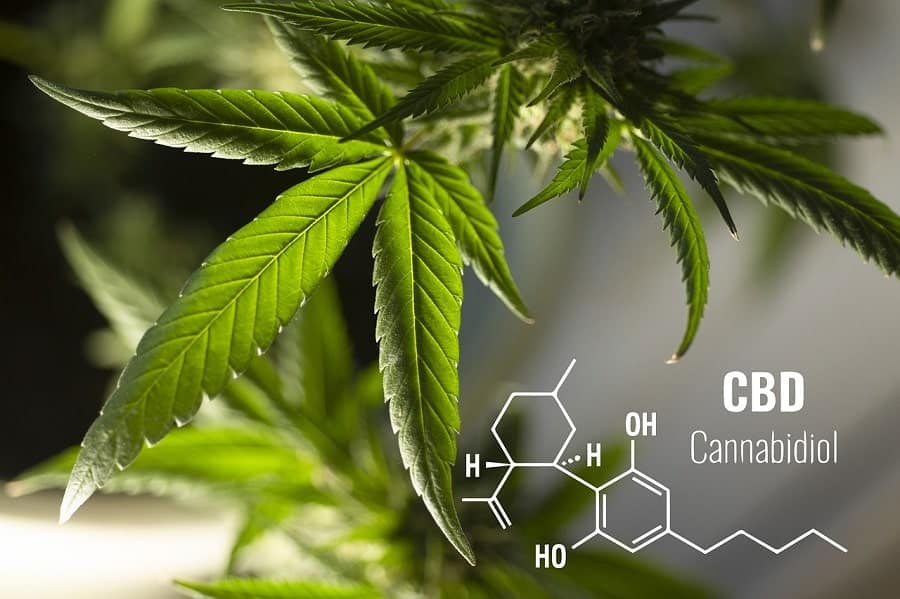 Instead, most researchers believe it interacts with the endocannabinoid system by preventing the breakdown of endocannabinoids, causing them to continue having an effect on your body for longer. Other experts studying CBD believe that it binds to a cannabinoid receptor which has not been discovered yet.
Instead, most researchers believe it interacts with the endocannabinoid system by preventing the breakdown of endocannabinoids, causing them to continue having an effect on your body for longer. Other experts studying CBD believe that it binds to a cannabinoid receptor which has not been discovered yet.
If you still have questions about cannabinoids and how to use them you can always consult with our friendly staff at your local marijuana dispensary.